1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| #include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print(int& Ele)
{
cout<<Ele<<" ";
}
void main()
{
list<int> L1,L2,L3,L0;
L1.push_back(1);
L1.push_back(5);
L2.push_back(2);
L2.push_back(3);
L3.push_back(7);
L3.push_back(8);
L0.push_back(9);
L0.push_back(-1);
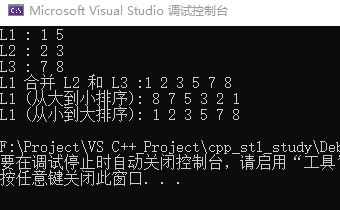
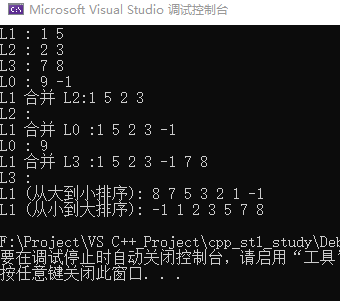
cout<<"L1 : ";
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L2 : ";
for_each(L2.begin(),L2.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L3 : ";
for_each(L3.begin(),L3.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L0 : ";
for_each(L0.begin(),L0.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L1 合并 L2:";
L1.splice(L1.end(),L2);
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L2 : ";
for_each(L2.begin(),L2.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L1 合并 L0 :";
L1.splice(L1.end(),L0,(++L0.begin()));
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L0 : ";
for_each(L0.begin(),L0.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L1 合并 L3 :";
L1.splice(L1.end(),L3,L3.begin(),L3.end());
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"L3 : ";
for_each(L3.begin(),L3.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
L1.sort(greater<int>());
cout<<"L1 (从大到小排序): ";
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
L1.sort();
cout<<"L1 (从小到大排序): ";
for_each(L1.begin(),L1.end(),print);
cout<<endl;
}
|