sortledton
1. introduction
动态数据集上的图处理在许多应用领域越发重要,如推荐系统和欺诈检测等。现今,许多场景下都需要进行大规模的图计算,如图分析(analytics),图模式匹配(graph pattern matching, GPM), 图遍历(tranversals).而这些图计算的数据集是动态变化的,随时都在进行更新。 创建这样一个系统仍然是一个未解决的问题,其根源就是没有底层数据结构既能保证高效率的事务更新,又能有效处理各种各样的图工作负载(比如模式匹配、图遍历就是不同的工作负载)。这篇文章就是要解决这个问题。 为支持分析工作负载(如page rank)和图遍历(单源最短路径)需要支持快速扫描。为了支持模式匹配(如triangle counting),数据结构需要有序to enable fast intersections。为了保证更新速度,该数据结构需要支持动态更新。为了保证并发,需要实现多版本。
2. background
动态图上的图工作负载主要有三类:analytics(Page rank),grapha pattern matching(triangle count), graph traversals(single-source-shortest path),怎么在动态图上支持所有的workload是一个问题。
2.1 problem
为了解决上述问题,有两个关键的challenges。
第一个挑战:
- all workloads require fast scannilng of neighborhoods
- high throughput of new deges requires fast insertions
- GPM needs intersection.
scan+insertion可以使用vector,但是求交集的复杂度是O(M*N);
scan+intersection可以使用有序数组,但是其插入很慢
insertion+intersection可以使用hash set,但是 hash sets have empty slots which require the evaluation of apredicate for each scanned element
第二个挑战
并发执行
2.3 Graphalytic Benchmake
WCC:weakly connected component
PR: PageRank
CDLP:community detection via label propagation
BFS: breadth-first search
SSSP: weighted single-source shortest path
LCC: local clustering co-efficient
3. Requirements and design goals
Four memory access patterns:
- sequential access to the neighborhoods of all vertices
- sequential access to the edges within a neighborhood
- random access to algorithm-specific properties, e.g., scores for PageRank or distances for BFS
- random access to the neighborhoods of all vertices.
3.1 Sequential Vertex Access
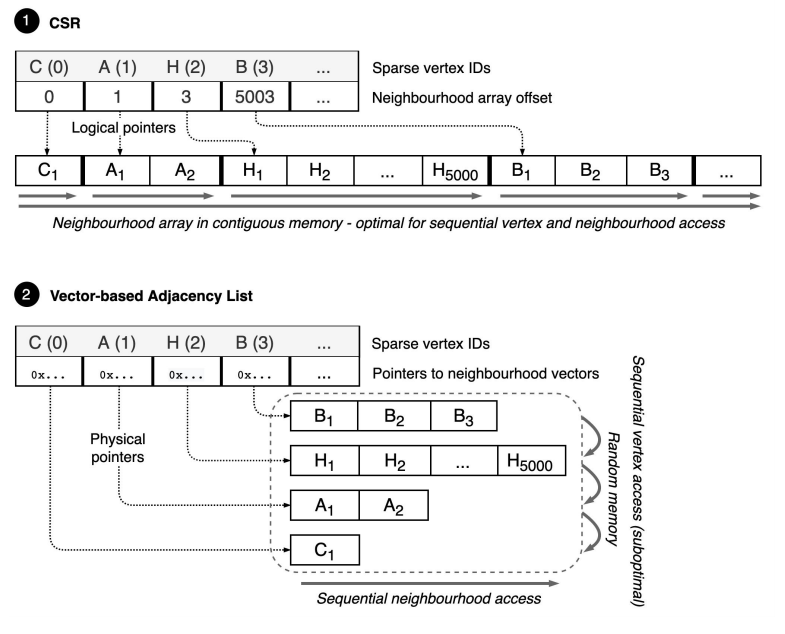
第一种用一个大的数组来存所有的邻居节点,第二种每一行都是一个vector,其内存分配是随机的,而不是连续的。
3.2 sequential neighborhoods access
先说明下sequential vertex access 和sequential neighborhoods access的区别(个人理解):
sequential vertex也就意味着所有的顶点访问都可以连续内存,而sequential neighborhood只是某个顶点的neighborhoods的是在连续的内存区域。对应上面图的1和2.
We conclude that optimal sequential neighborhood access can be supported by set data structures with at least 256 edges per block.